Testing of inks containing carbon nanotubes printed on various polymer films
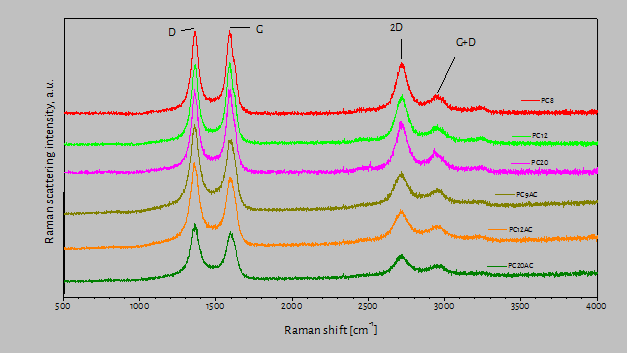
The object of the tests was conductive ink containing multiwall carbon nanotubes. The ink was printed on polycarbonate film (PC) and copolymer polycarbonate and polyacrylate film (PC-AC). The aim of the test was to find, on which base the ink layer shows best adhesive properties. Therefore, they used Raman spectroscopy. The spectra measured contain visible […]
The object of the tests was conductive ink containing multiwall carbon nanotubes. The ink was printed on polycarbonate film (PC) and copolymer polycarbonate and polyacrylate film (PC-AC). The aim of the test was to find, on which base the ink layer shows best adhesive properties. Therefore, they used Raman spectroscopy. The spectra measured contain visible strands typical of multiwall carbon nanotubes. The strand marked as D on the figure is excited by defects in nanotube walls. The surface depth of the defects in nanotubes printed on copolymer polyacrylate film is 20% greater than in case of polycarbonate film. Additionally, the positions of D and 2D strands in nanotubes printed on the polyacrylate film are much more shifted to greater frequencies, which proves that there are stronger dielectric interactions between ink and the film with polyacrylate component. Based on the tests performed, we can recommend films with added polyacrylates as a better base for conductive inks based on carbon nanotubes than in case of polycarbonate films.